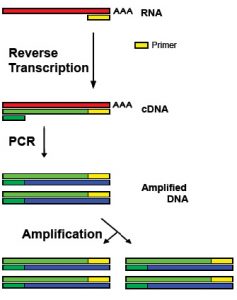
 RT-qPCR combines the amplification of small complementary DNA (cDNA) sequences with their accurate quantification by fluorescence measurement. This technique is widely distribute to adequately monitor gene expression levels, even in high throughput and at a relatively low cost.
RT-qPCR combines the amplification of small complementary DNA (cDNA) sequences with their accurate quantification by fluorescence measurement. This technique is widely distribute to adequately monitor gene expression levels, even in high throughput and at a relatively low cost.
Advantages of RT-qPCR
- Accurate gene expression quantification
- High-throughput sample analysis possible
RT-qPCR workflow
You provide us with samples of cells resuspended in an RNA extraction solution (e.g. Trizol) or directly with RNA extracts. When starting from Trizol samples, the RNA isolation will be performed by means of a phenol-chloroform extraction, followed by several washing steps through an RNeasy Mini column, a DNase treatment to remove any potential genomic DNA contamination and the eventual RNA elution. Hereafter, the resulting RNA-extract will undergo reverse transcription to yield the cDNA. Several quality control steps are included along the protocol.
The obtained cDNA will subsequently be analyzed with the adequate RT-qPCR assay (probe- or SYBR Green-based) depending on your experimental question. Several reference genes can be included in this assay, making correct data normalization afterwards possible. All assays are run on a 96-well or a 384-well Roche LightCycler 480.