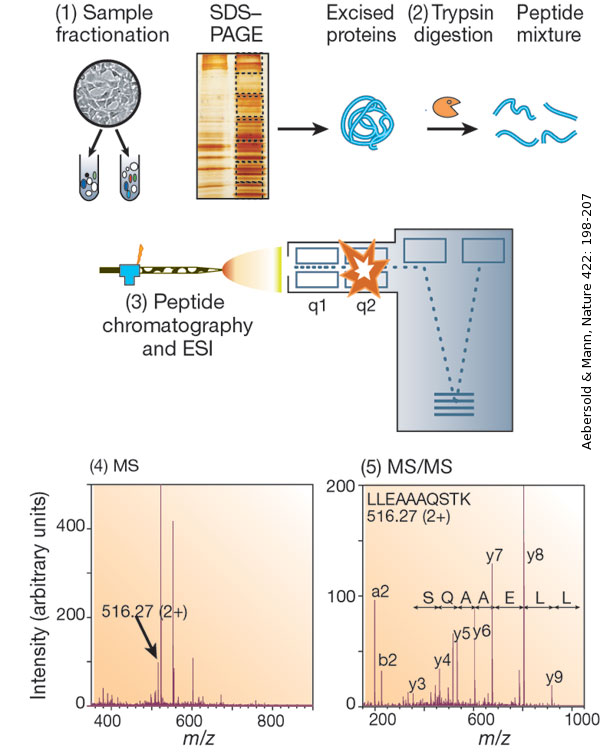
 Gel electrophoresis is used to separate protein mixtures. This can be done in one dimension (1D), based on the molecular weight of the proteins, or in two dimensions (2D), based on their iso-electric point, followed by an additional molecular weight separation. After staining and imaging of the gel, little gel pieces can be excised. The protein content can be digested into peptides and identified by means of liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS).
Gel electrophoresis is used to separate protein mixtures. This can be done in one dimension (1D), based on the molecular weight of the proteins, or in two dimensions (2D), based on their iso-electric point, followed by an additional molecular weight separation. After staining and imaging of the gel, little gel pieces can be excised. The protein content can be digested into peptides and identified by means of liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS).
2D gels can also be compared to each other by means of the PDQuest software and differences in expression can be reported.
Additionally, 1D and 2D gels can also be used for Western blotting and subsequent immunodetection. This setup is commonly used for the identification of immunoreactive proteins.
Advantages of gel-based proteomics
- Separation of proteins prior to digestion leads to a higher number of identified proteins
- Can be used to identify immunoreactive proteins (in combination with Western blotting)
- Can be used to separate a protein of interest from other (abundant) proteins that can interfere with the identification step.
Workflow
You provide us with your protein(mixture) of interest. The customer can decide whether only 1D or 2D is preferred. The range of the iso-electric focusing and the percentage of the gel can also be determined by the customer.
For protein separation by gel (SDS-PAGE), the composition of the buffer should be mentioned. Detrimental for gel electrophoresis is the presence of salt in your protein mixture. For 2D separation, no anionic or cationic detergents (such as SDS) can be present.